Knee ligament reconstruction
Knee surgery
Atteintes des ligaments ou des ménisques, arthrose, dysfonctionnement des rotules… Des pathologies typiques de la chirurgie du genou qui nécessitent des gestes thérapeutiques pour retrouver toute la fonctionnalité de l’articulation.

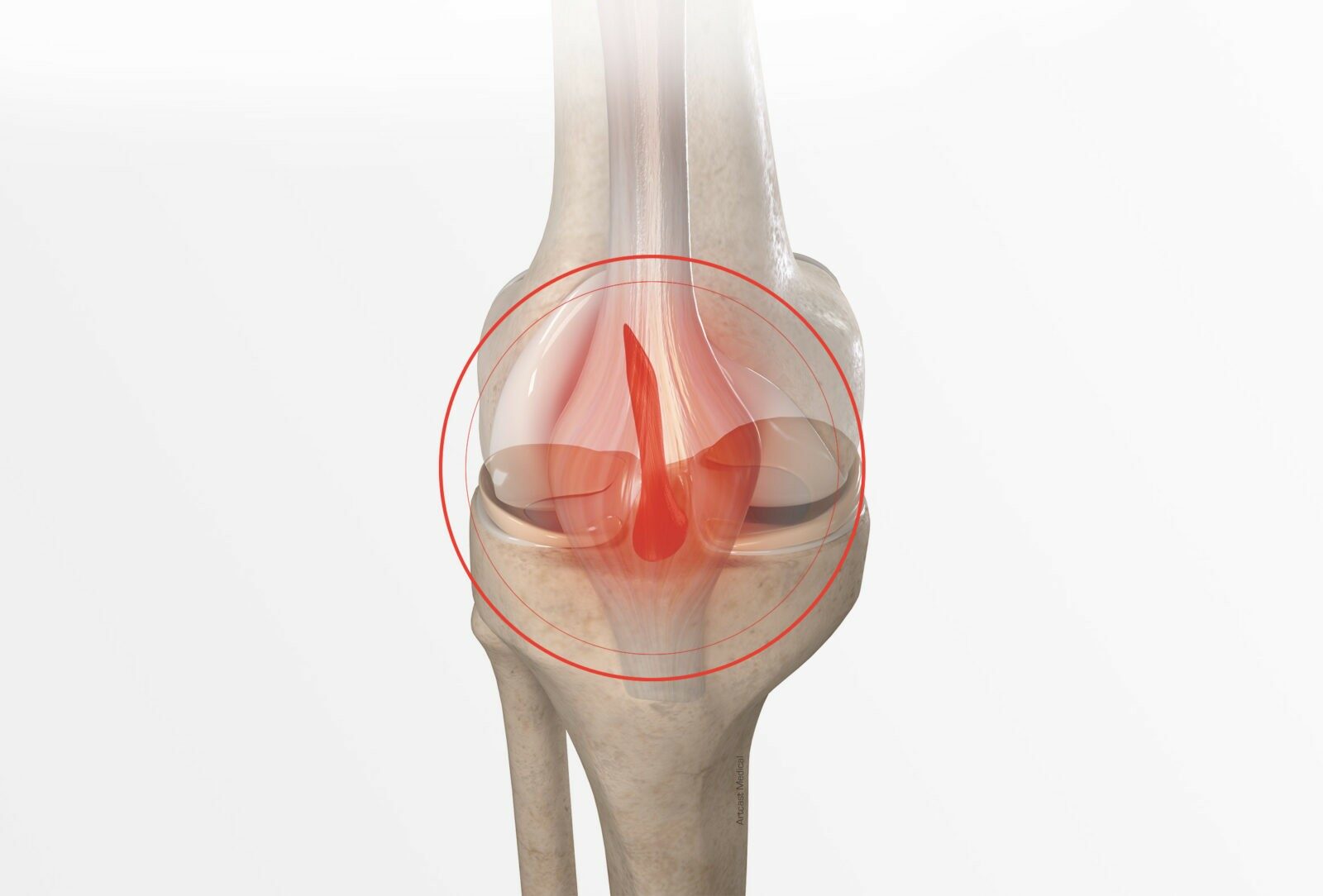
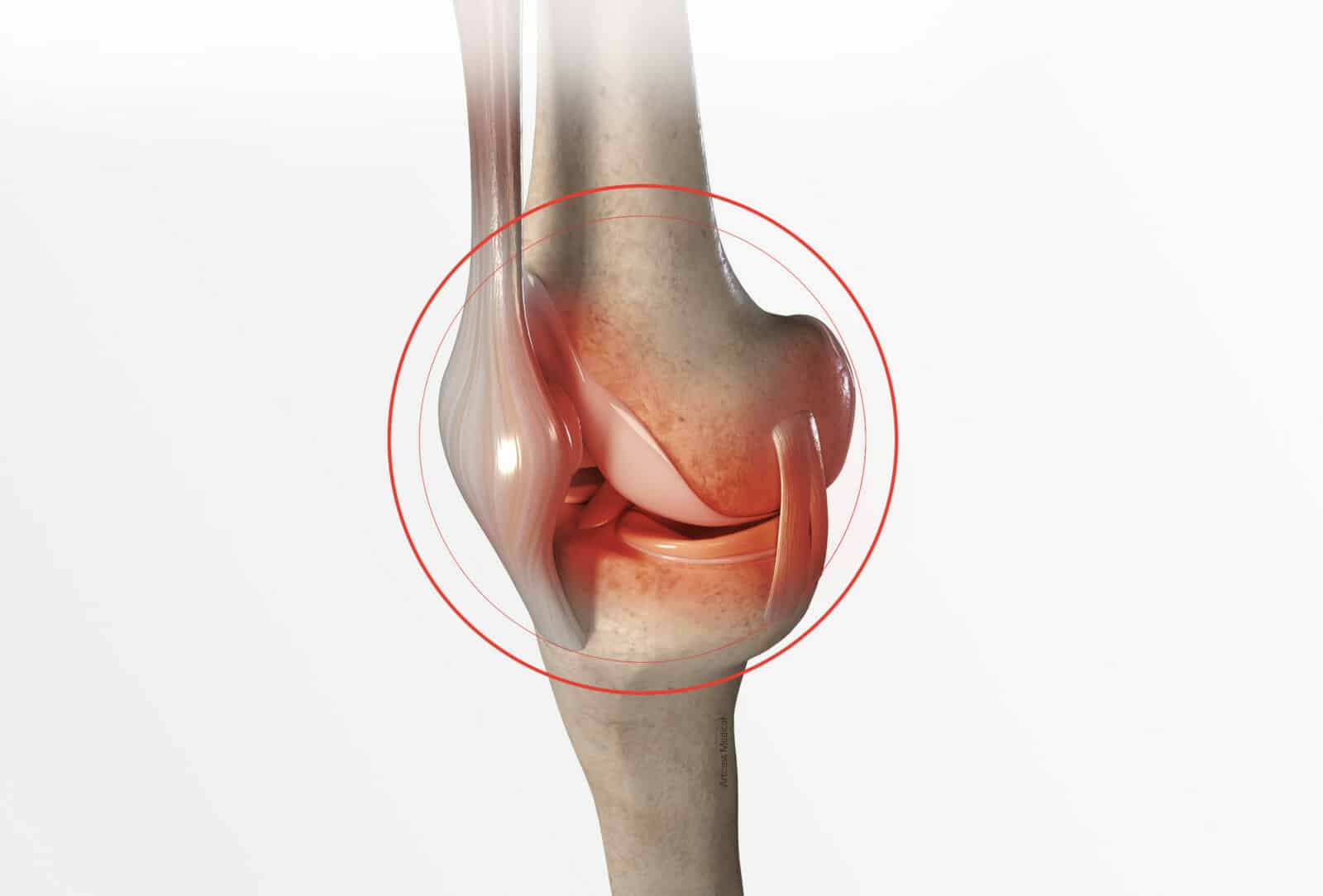
Knee ligament reconstruction
During physical exertion or following a trauma, the ligament in the knee can rupture. However, the anterior cruciate ligament will not heal spontaneously and so the surgeon carries out knee ligament reconstruction.
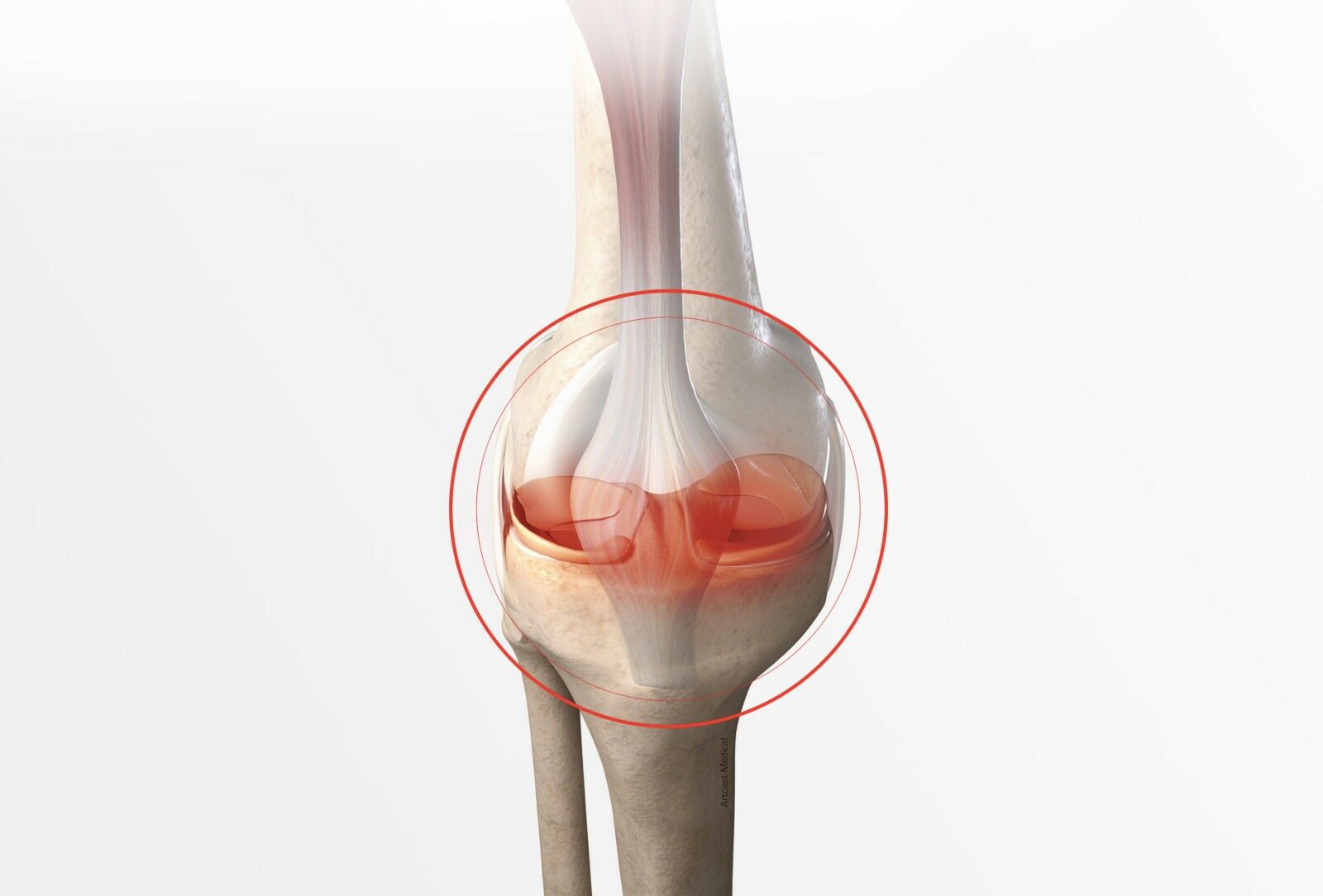
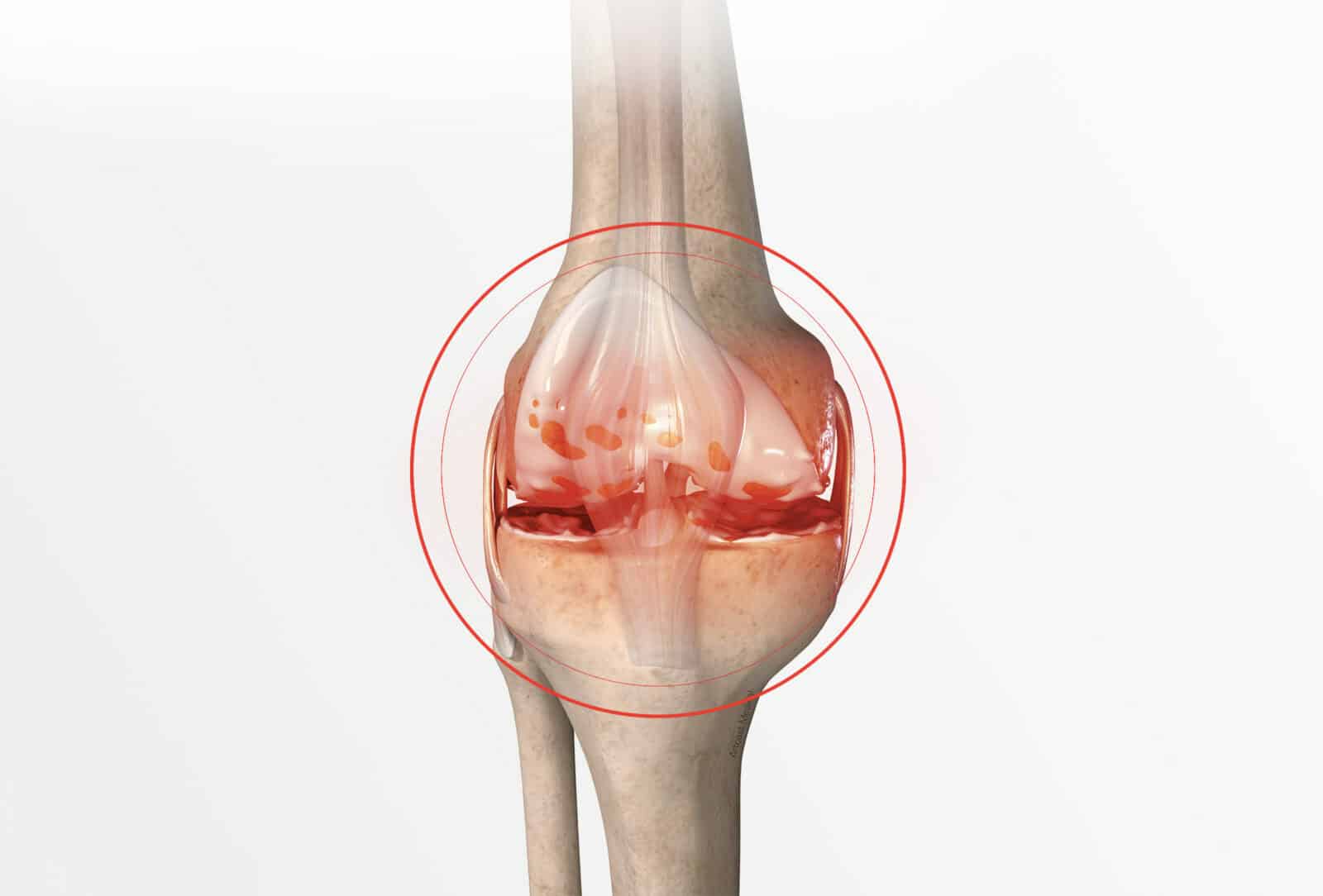
Meniscal surgery
Meniscal surgery
The menisci are cushions which act as shock absorbers to protect the knee. Over time they get thinner, become more fragile and can suffer damage during physical activity or due to a trauma. Meniscal surgery is performed arthroscopically (keyhole surgery): tiny incisions are made to repair the damaged meniscus.
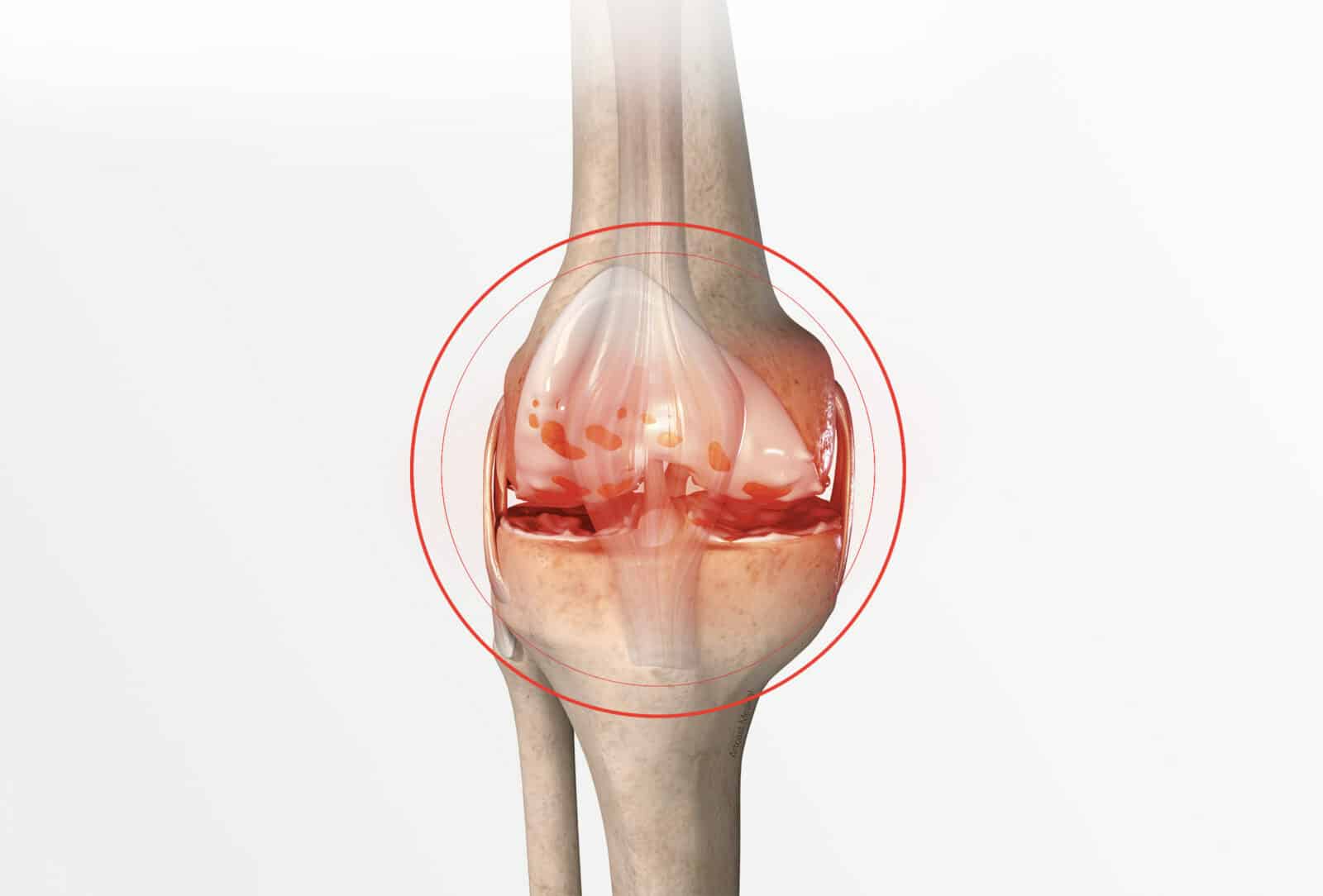
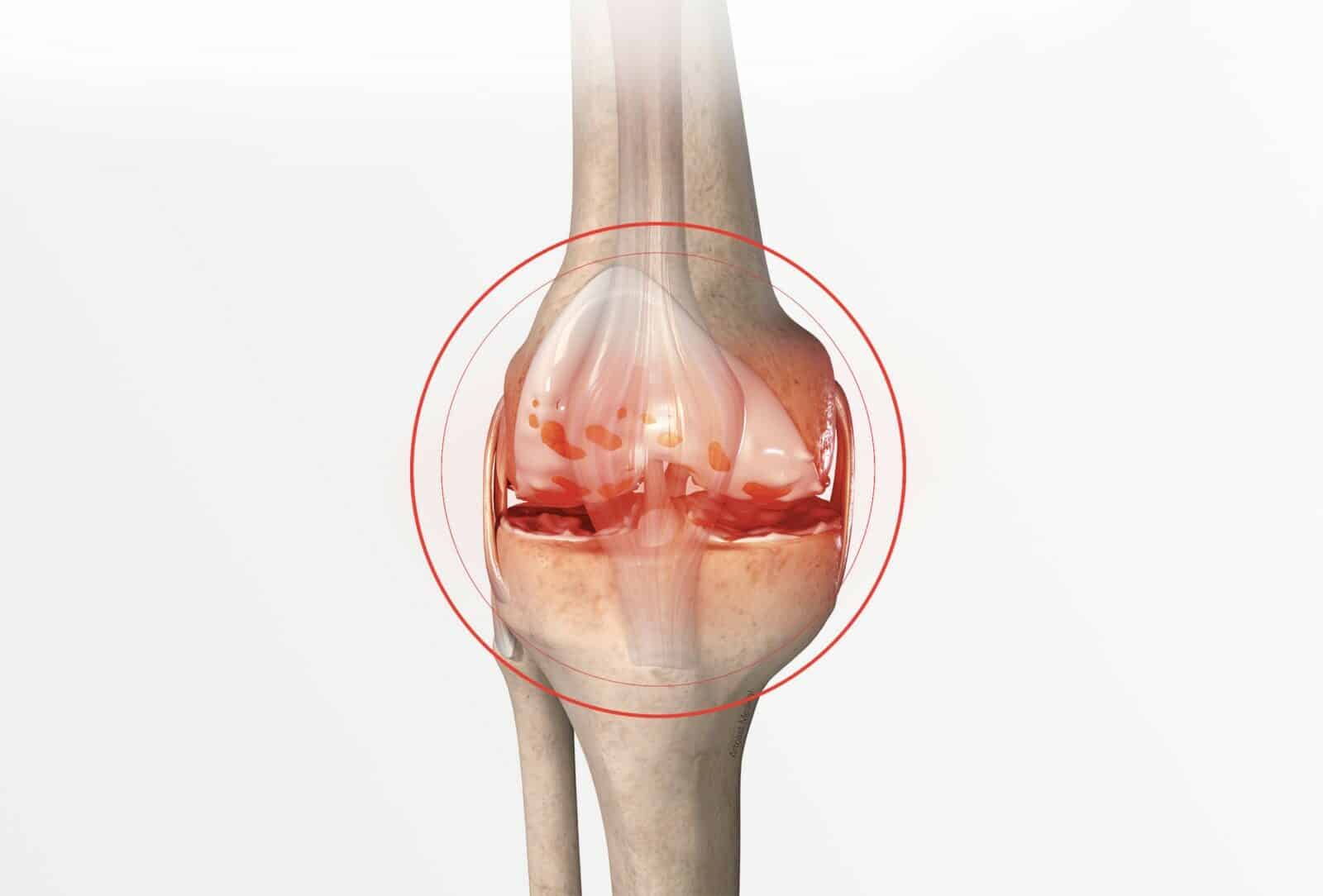
Total knee replacement
Total knee replacement
Osteoarthritis is the deterioration and wear of the cartilage. It affects the knee, among other things, causing pain and difficulty in carrying out everyday activities or certain movements. With knee replacement, the joint recovers freedom of movement and is no longer painful.
Unicompartmental knee replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement
In the case of osteoarthritis, only one compartment of the knee joint may be worn. The surgeon therefore proposes a partial knee replacement, that is, the replacement of only the damaged parts of the joint with a knee implant.
Patella realignment
Patella realignment
When patella dysfunction is observed with symptoms including discomfort, pain, swelling or locking, the therapeutic indication is patella realignment. This knee surgery realigns the joint by positioning the patella properly in the centre of the trochlear groove, that is, the knee.
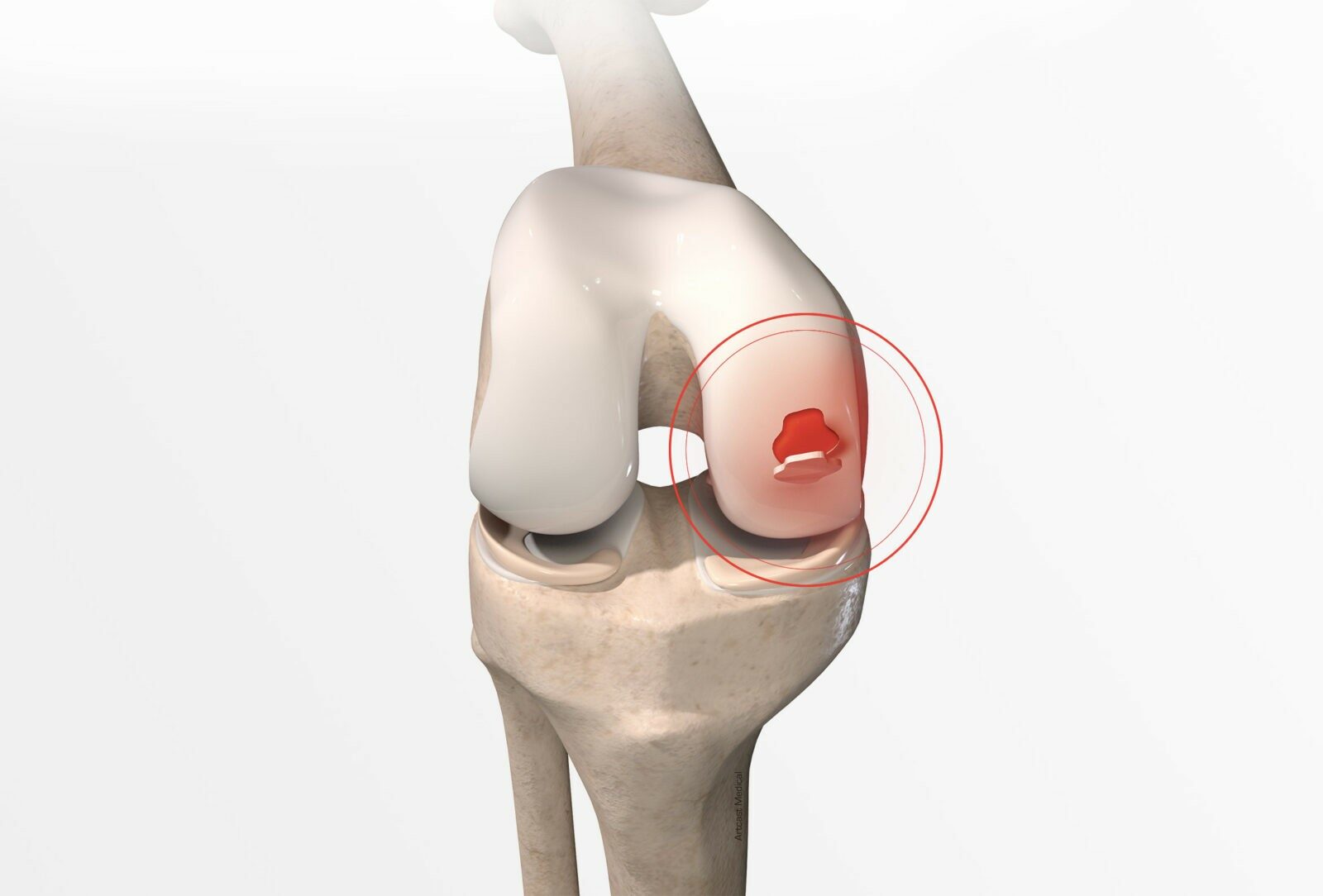
Knee cartilage surgery
Knee cartilage surgery
Injuries, recurrent physical exertion or imperfect growth are the main causes of knee cartilage damage resulting in pain, swelling and discomfort. Knee cartilage surgery can help decrease this damage.
Tibial valgus osteotomy
Tibial valgus osteotomy
To treat knee osteoarthritis, one procedure consists in operating on the superior end of the tibia to bring the mechanical axis through the centre of the knee. A valgus osteotomy, performed under x-ray control, involves the placement of a plate until the bone heals.
Revision knee replacement
Revision knee replacement
Knee replacement gives the joint a second life. Nevertheless, the implant can wear over time, sometimes resulting in loosening. It then no longer ensures its function correctly so the surgeon replaces the knee prosthesis in order to restore the freedom of movement without pain.