Podiatry
During the consultation, the podiatrist will assess with you the treatment that is most appropriate for you.
During the consultation, the podiatrist will assess with you the treatment that is most appropriate for you.
Podiatry
First, the practitioner asks the patient a series of questions regarding their medical and surgical history in order to uncover the reason for the consultation and determine the source of the pain. If the patient has already undergone any examinations (x-ray, MRI, ultrasound, scan), it is important they bring the images to the appointment to corroborate the diagnoses established at the end of the session.
Next, the practitioner observes the patient in supine position, then standing (static and dynamic).
The practitioner looks for different painful spots and then conducts a more detailed examination by palpating the various tissues (skin, ligaments, and muscles) to determine the tissues linked to the pain.
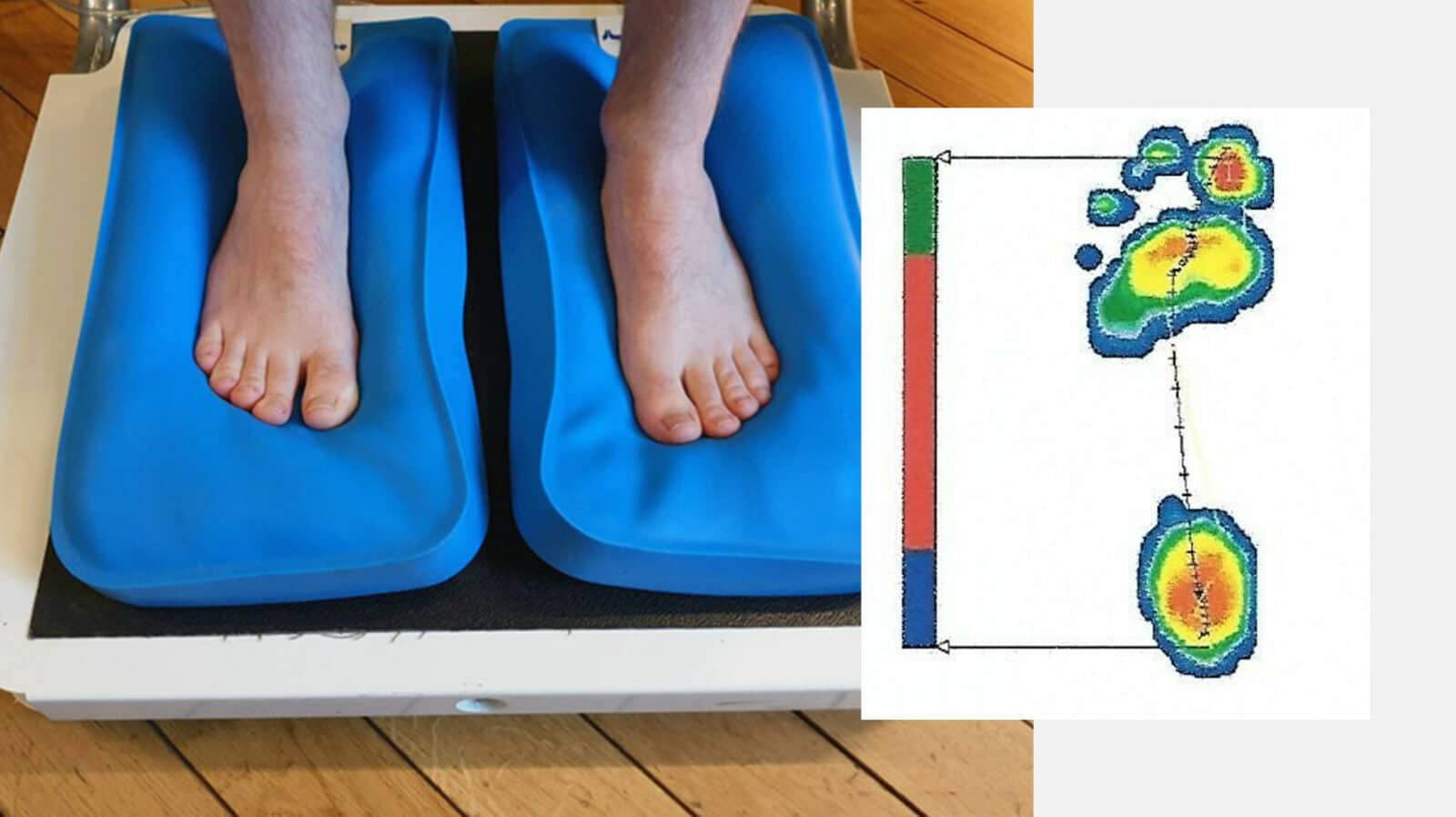
During the static assessment using a posturoscope as well as a podoscope, the overall posture of the patient can be observed in different planes (cf. photos below).
The examination then continues with a dynamic assessment on a treadmill whether the patient is sporty or not. Video analysis is used to assess walking and/or running. The image is shown on a TV screen and the patient’s biomechanics can thus be explained in real time. Using video analysis, it is possible to distinguish any variations in torsion measurements that can occur.
For athletes, the podiatrist will endeavor to expand on certain issues such as the intensity of their sports activities, injuries (old or recent), equipment, and how the sports gestures are performed. It is therefore essential to bring the sports shoes used during training and during competitions.
This examination is conducted on a baropodometric plate on which there are thousands of new generation sensors to analyze, confirm, and quantify the observations obtained previously and to accurately measure plantar pressure distribution. The podiatric assessments can also be archived and thus the progression over time can be monitored.
The examination on the platform is conducted in a static position, then walking. This appliance helps the patient understand better the biomechanics through images representing their foot-to-ground contact.
The practitioner must assess the space available in the sports shoes and/or town footwear to best adapt the device that will be proposed.
At the end of the session, the practitioner will give the patient some advice to assist them in selecting the best shoes for their condition.
The patient then leaves with the test results (which are also sent to the prescribing physician).
As the aim is to monitor the progression and the improvement of the reason for consulting, several follow-up appointments will be proposed, of which the first one month later. The pain and adaptation to the insoles will be assessed.
Bring your health insurance card (carte vitale), the medical prescription, your latest x-rays, the shoes you usually wear and your sports shoes, if needed.
The feet are the static and dynamic base, and an imbalance will have consequences on muscular work and muscle tone, as well as on joint positions of the feet, knees, pelvis, and back in the short and medium term.
Deformities of the lower limbs in children are a cause for concern and a common reason for consulting a podiatrist. These deformities are quite often part of the normal growth pattern of the lower limbs :
Childhood conditions and diseases
Sever’s, Köhler’s, Freiberg’s, Renander’s, Osgood-Schlatter’s, Legg-Calvée-Perthes, Scheuermann’s, intoeing…
Teenagers with their growth peak, their sport, their shoes, and their muscle stiffness also require special attention.
After a certain number of years of being diabetic (between 10 and 15 years), some patients may develop neuropathy, in other words, the quasi-total insensitivity of the plantar side of the foot.
In conjunction with a deformity and/or arteritis, the patient is at great risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer.
The role of the podiatrist is to diagnose the patient’s podiatric risk on a scale of 0 (no neuropathy, no risk) to 3 (the patient has already had a wound that lasted over three weeks and required medical footwear as well as foot orthotics).
According to the risk, the podiatrist must establish the most appropriate therapy including :
Today, podiatrists have modern methods at their disposal to conduct both static and dynamic clinical assessments of athletes. The podiatrist uses effective, comfortable materials to make plantar orthotics adapted to all types of sports and footwear.
The podiatrist, therefore, has a legitimate role in the medical team of elite athletes. Podiatric treatment that modifies pathological posture can be combined with other treatments.
Numerous static disorders of the lower limbs are totally or partially linked to sports pathologies:
Skin and ungual disorders
Hyperkeratosis, subungual hematomas, phylcentule (blisters), overheating…
Osteo-articular and musculo-tendinous disorders
Orthopedic insoles are part of the non-surgical treatment of numerous traumatic and rheumatic disorders of the lower limbs.
Ankle instability, chronic sprains, tibial periostitis, peroneal tendonitis, tibialis posterior tendonitis, Achilles tendonitis…
Osteoarthritis, Pes anserinus tendonitis, Tensor fasciae latae muscle tendonitis (runner’s knee, iliotibial band syndrome), patellar tendonitis, femoropatellar chondropathy, genu valgum, genu varum, patellar misalignment…
Trochanteritis, pubalgia, sacro-iliac pain…
Chronic lower back pain, cervicodynia, migraines, attitude scoliosis, balance disorders…
During the consultation, the podiatrist will assess with you the most appropriate treatment.
The insoles designed by the latter are made-to-measure and will help achieve ideal static and dynamic function.
They prevent, reduce and even correct numerous chronic or acute disorders of the foot, knee, pelvis or spine.
These insoles can be worn at any age in casual or sports shoes.
Comfort insoles molded to the shape of the foot can also be made.
The podiatrist can also design silicone devices called ‘orthoplasties’ in order to modify the position of the toes and to protect the foot from hyper-pressure, which is often painful. In children, they can definitively correct some toe misalignments.
Laissez votre commentaire